Carbide ceramic
SILICON CARBIDE (SIC)
Materials on the basis of silicon carbide (SIC) belong to the most important carbide ceramics. Depending on the manufacturing process and the type of bonding SC ceramics differ:
| Open porous SC | Dense SC |
|---|---|
| Siliceous bonded SIC | Silicon infiltrated SC (SSIC) |
| Recrystallized SIC (RSIC) | Sintered SIC (SSIC) |
| Nitride res. oxynitride bonded SIC (NSIC) | hot (isostatically) pressed SC (HPSIC, HIPSIC) |
They stand out for their typical properties:
- High to very high strength
- Resistance to corrosion up to a very high application temperature
- Excellent mechanical high temperature properties
- Very good thermal shock resistance
- Low thermal expansion
- Very high thermal conductivity
- High wear resistance
- High hardness
- Semiconductor properties
SINTERED SILICION CARBIDE (SSIC)
Sintered silicon carbides is made from SC finest powder plus sinter additives, and is sintered at 2000 to 2200 °C in a controlled atmosphere. Its outstanding features are:
- Very high strength and
- Extremely high resistance to corrosion.
These excellent properties are effectively supplemented by
- The typical high thermal shock resistance,
- Thermal conductivity,
- Wear resistance and
- Hardness similar to a diamond.
SSIC is especially suitable for applications with high demands e.g.
- Slide ring washers for lye pumps,
- High-temperature burner nozzles or
- Kiln furniture.
REACTION BONDED SILICON INFILTRATED SILICON CARBIDE (SSIC)
SSC consists to 85 - 94% of SC and correspondingly 15 - 16% of metallic silicon. There is no shrinkage during the sintering process because of the composite manufacturing process. This is why extraordinary large components with exact dimensions can be manufactured. The application temperature is limited to approx. 1380 °C due to the share of metallic silicon.
SSIC has a 
- High strength and corrosion resistance,
- Combined with excellent thermal shock resistance and resistance to wear.
SSIC is high suitable for the production of
- High-load kiln furniture, kiln components,
- Wear and corrosion resistant machine components and
- Heating elements
RECRYSTALLIZED SILICON CARBIDE (RSIC)
RSIC is a pure SIC material with an open porosity of approx. 11 to 15 %. As a result it has in comparison to the dense SIC ceramics a lower strength, but an
- Excellent thermal shock resistance.
The non-shrinking manufacturing process enables the production of large size RSIC components which are then mainly used as kiln furniture with
- High load-bearing capacity.
The maximum application temperature lies between 1600 and 1650 °C
NITRIDE BONDED SILICON CARBIDE (NSIC)
Analogue to RSIC this is also an open porous material with approx. 12 to 15% porosity. During a nitride process in which non-shrinking components are able to be manufactured, a green body made of SIC is nitrided in a nitrogenous atmosphere at 1500 °C. In comparison to RSIC the porosity is finer and seals itself with a very thin glaze at
- High temperatures.
This oxidation process allows the use of NSIC components as kiln furniture with a
- High load-bearing capacity up to 1450 °C.
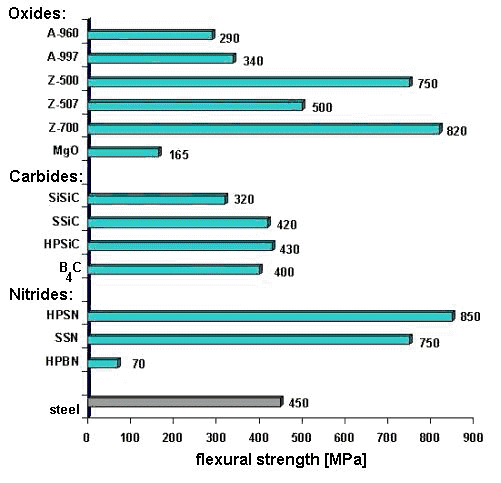
Comparison between oxide and non oxide ceramics: Flexural strength